- Dapatkan link
- Aplikasi Lainnya
- Dapatkan link
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Incomplete Kawasaki disease should be taken into consideration in case of all children with unexplained fever for more than 5 days associated with 2 or 3 of the main clinical findings of Kawasaki disease. Incomplete Kawasaki disease should be taken into consideration in case of all children.
 Diagnosis Treatment And Long Term Management Of Kawasaki Disease A Scientific Statement For Health Professionals From The American Heart Association Circulation
Diagnosis Treatment And Long Term Management Of Kawasaki Disease A Scientific Statement For Health Professionals From The American Heart Association Circulation
Atypical Kawasaki disease should be considered and testing should be initiated if the child has had 5 days of fever 39 C about 1022 F plus 2 of the 5 criteria for Kawasaki disease.

Atypical kawasaki disease criteria. The AHA and AAP recommend that the phrase atypical Kawasaki disease be reserved for patients who have a problem such as renal impairment that generally is not seen in KD. The fever typically lasts for more than five days and is not affected by usual medications. Kawasaki disease KD also called Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome is an acute systemic vasculitis of.
Lab testing if HP consistent with complete or incomplete KD. Particularly coronary artery aneurysms. It is a form of vasculitis where blood vessels become inflamed throughout the body.
Coronary artery abnormalities on transthoracic echocardiography. Until a definitive test is available clinical judgment is required in the diagnosis of atypical Kawasaki disease. History Physical Clinical Criteria.
Although not part of the formal diagnostic criteria the 2017 AHA guidelines emphasised the utility of Z scores to reflect standardised dimensions of coronary arteries normalised for body surface area BSA to allow for classification Manlhiot C Millar K Golding F et al. Kawasaki disease KD formerly called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome is one of the most common vasculitides of childhood. Improved classification of coronary artery abnormalities based only on coronary artery z-scores after Kawasaki disease.
Laboratory tests are not diagnostic but may be done to exclude other disorders. The term atypical Kawasaki disease was initially coined to describe patients with coronary artery abnormalities whose illness did not meet the strict criteria for classic Kawasaki disease. Diagnostic criteria for Kawasaki disease are fever and at least four of the five additional clinical signs.
Diagnostic criteria CRASH and burn the heart. Can be made in a patient who presents with a prolonged high fever and meeting at least four of five criteria including polymorphous rash mucosal changes extremity changes including swelling andor palmar and. It is typically a self-limited condition with fever and manifestations of acute inflammation lasting.
CRP C-reactive protein. Assess for presence of clinical criteria at any time during current febrile illness. Diagnostic criteria for Kawasaki disease are fever and at least four of the five additional clinical signs.
ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Serum albumin 3 gdL Hypoalbuminemia Supplemental laboratory criteria not required for diagnosis to help with atypical Kawasaki. Kawasaki Disease is an inflammatory process that can affect all blood vessels and result in cardiac complications.
KD also occurs rarely in adults. CBC with diff Complete blood count CBC with differential white blood cell WBC count. Kawasaki disease is a syndrome of unknown cause that results in a fever and mainly affects children under 5 years of age.
Consider lab testing if 3 days of fever and strong clinical suspicion for KD. Sonobe and Kawasaki 2 proposed that the diagnosis of atypical Kawasaki disease be restricted to those children who have 3 or 4 of 5 of the clinical criteria plus coronary artery vasculitis. Awasaki disease KD is an acute self-limited fe-brile illness of unknown cause that predominantly affects children disease in children in.
This case report describes an atypical or incomplete presentation of Kawasaki Disease. Intravenous immune globulin is known to be safe and its early use in patients with suspected atypical Kawasaki disease is appropriate. Kawasaki Disease Typical and Atypical Background.
Incomplete KD should be considered in all children with prolonged unexplained fever associated with even a few of the principal clinical features of KD. Typical and atypical Kawasaki disease using AHA criteria Bai 2017 383 Hospital China Diagnosis of Kawasaki disease according to the Japanese Circulation Society Joint Working Group Japan Baker 2009 198 Hospital USA and Canada Typical and incomplete Kawasaki disease using AHA criteria. Alternative diagnostic criteria for classic Kawasaki disease Fever for at least five days and two or three principal features.
Kawasaki disease KD is an acute systemic vasculitis of childhood.
 Full Text Refractory Kawasaki Disease Diagnostic And Management Challenges Phmt
Full Text Refractory Kawasaki Disease Diagnostic And Management Challenges Phmt
 Algorithm For Evaluating Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Time Of Care
Algorithm For Evaluating Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Time Of Care
 Kawasaki Disease American Academy Of Pediatrics
Kawasaki Disease American Academy Of Pediatrics
 Kawasaki Disease Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome
Kawasaki Disease Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome
 Atypical Kawasaki Disease In 2 Months Old Infant Presenting With Aseptic Meningitis Semantic Scholar
Atypical Kawasaki Disease In 2 Months Old Infant Presenting With Aseptic Meningitis Semantic Scholar
 Atypical Kawasaki Disease In 2 Months Old Infant Presenting With Aseptic Meningitis Semantic Scholar
Atypical Kawasaki Disease In 2 Months Old Infant Presenting With Aseptic Meningitis Semantic Scholar
 Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
 Diagnosis And Management Of Kawasaki Disease American Family Physician
Diagnosis And Management Of Kawasaki Disease American Family Physician
 Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
 Classical Diagnostic Clinical Criteria Of Kawasaki Disease Prepared By Download Scientific Diagram
Classical Diagnostic Clinical Criteria Of Kawasaki Disease Prepared By Download Scientific Diagram
 Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
 Kawasaki Disease An Update Of Diagnosis And Treatment
Kawasaki Disease An Update Of Diagnosis And Treatment
 Table 2 From Kawasaki Disease An Update On Diagnosis And Treatment Semantic Scholar
Table 2 From Kawasaki Disease An Update On Diagnosis And Treatment Semantic Scholar
 Diagnosis And Management Of Kawasaki Disease American Family Physician
Diagnosis And Management Of Kawasaki Disease American Family Physician
 Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease 1 In The Absence Download Scientific Diagram
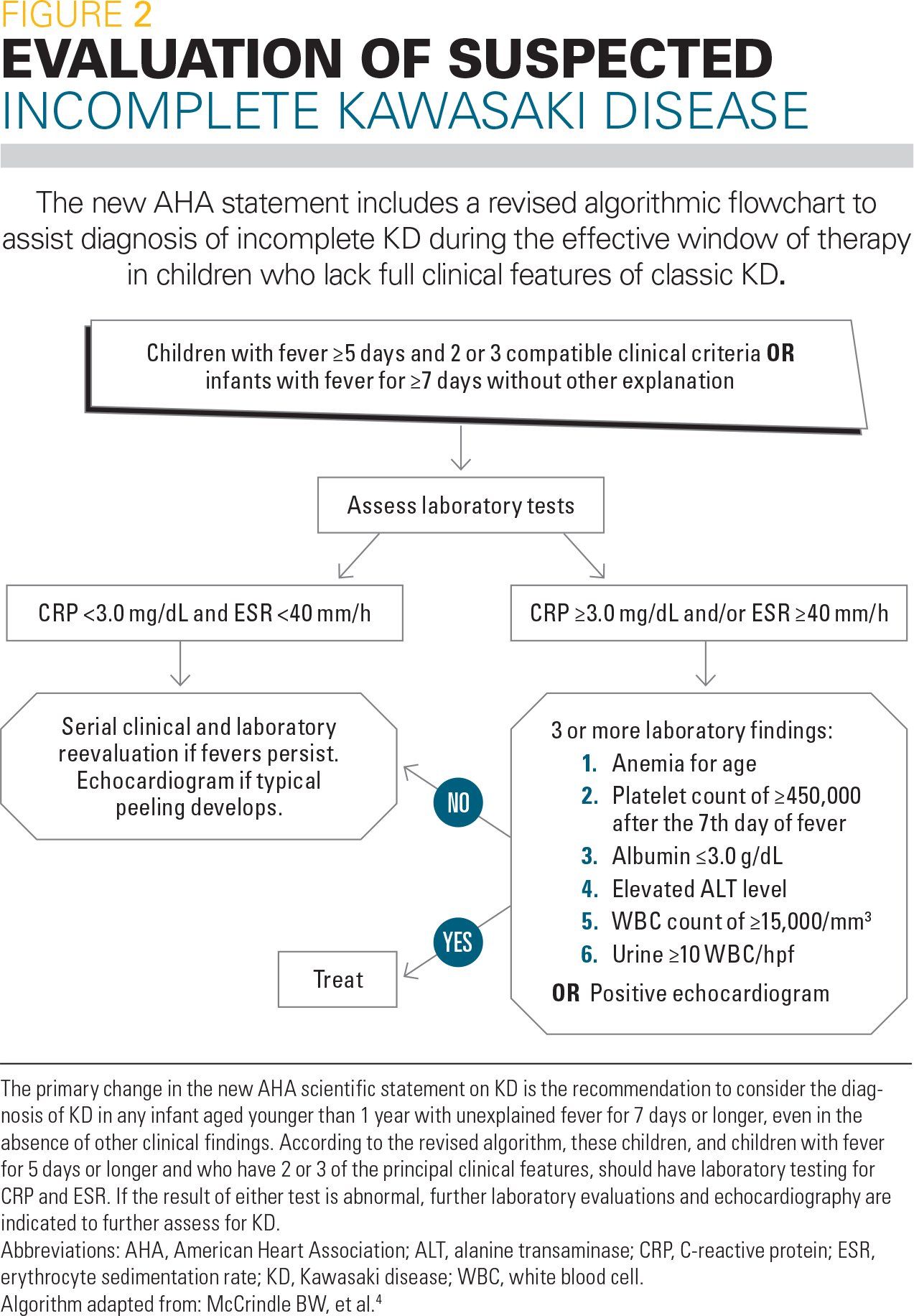 Kawasaki Disease Aha Statement And Recommendations
Kawasaki Disease Aha Statement And Recommendations
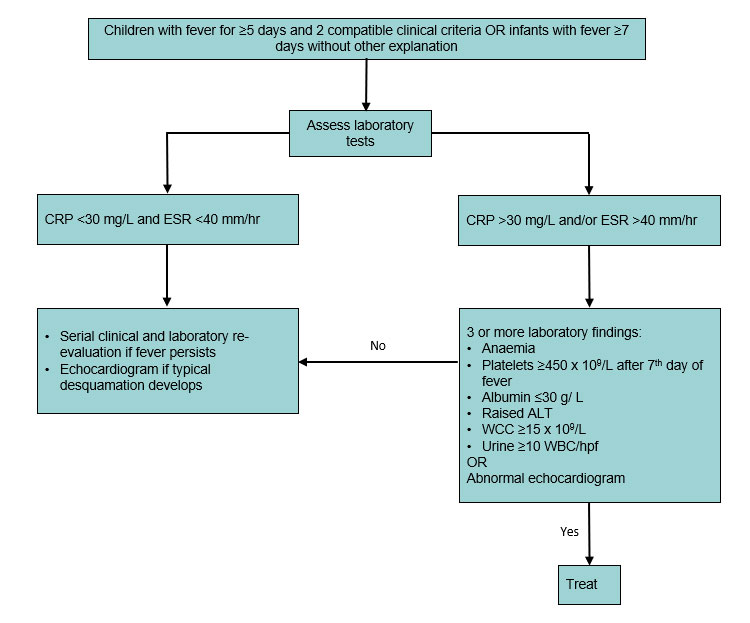 Clinical Practice Guidelines Kawasaki Disease
Clinical Practice Guidelines Kawasaki Disease
 Diagnosis And Management Of Kawasaki Disease American Family Physician
Diagnosis And Management Of Kawasaki Disease American Family Physician


Komentar
Posting Komentar